Guide to Grub Screws
What is a grub screw?
A grub screw is a type of headless screw used in precision applications where a discreet locking solution is required for an assembly. Grub screws employ a machine type thread to achieve this, for use with a tapped hole.
View all available Grubs Screw sizes and materials
What are Grub Screws used for?
|
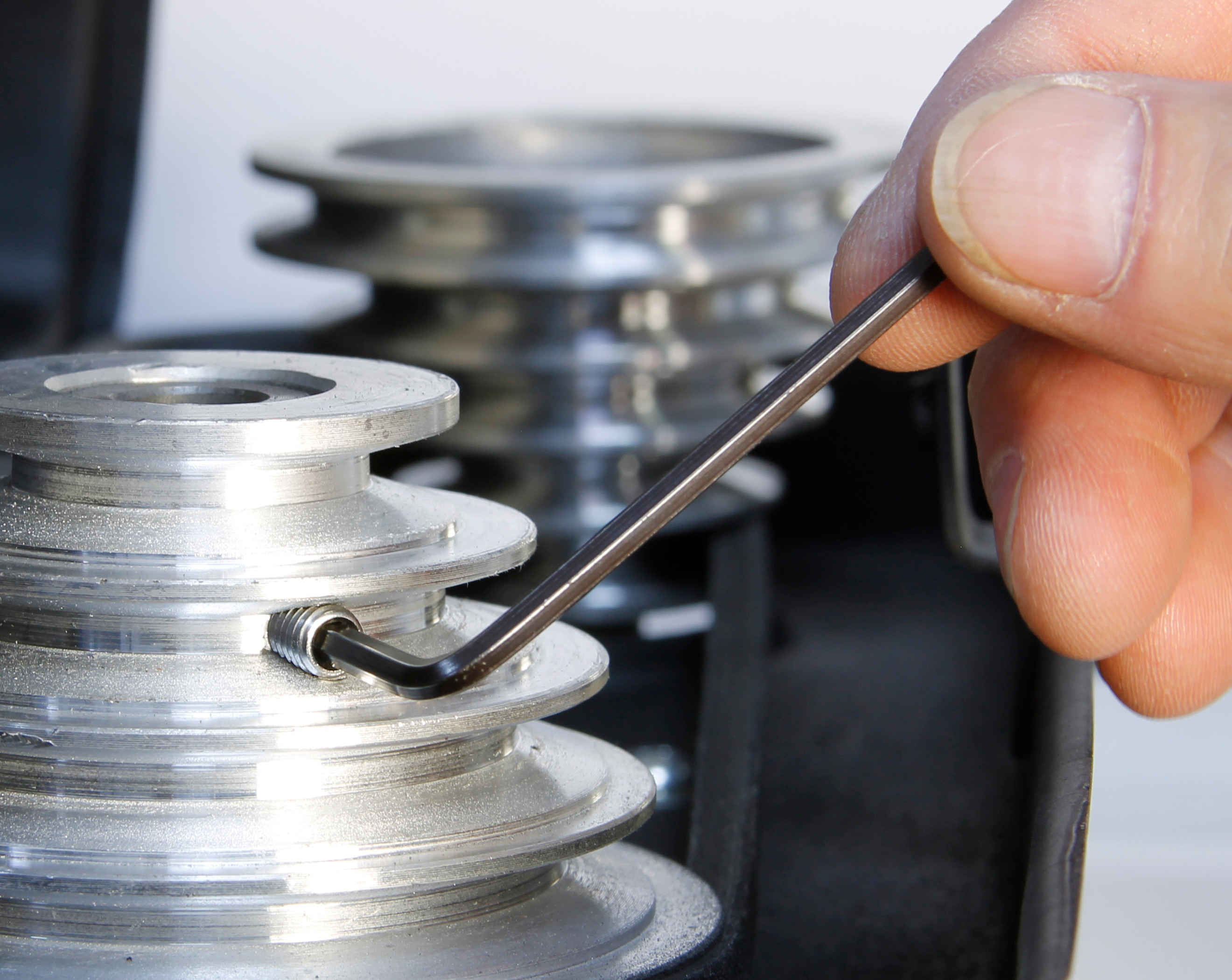
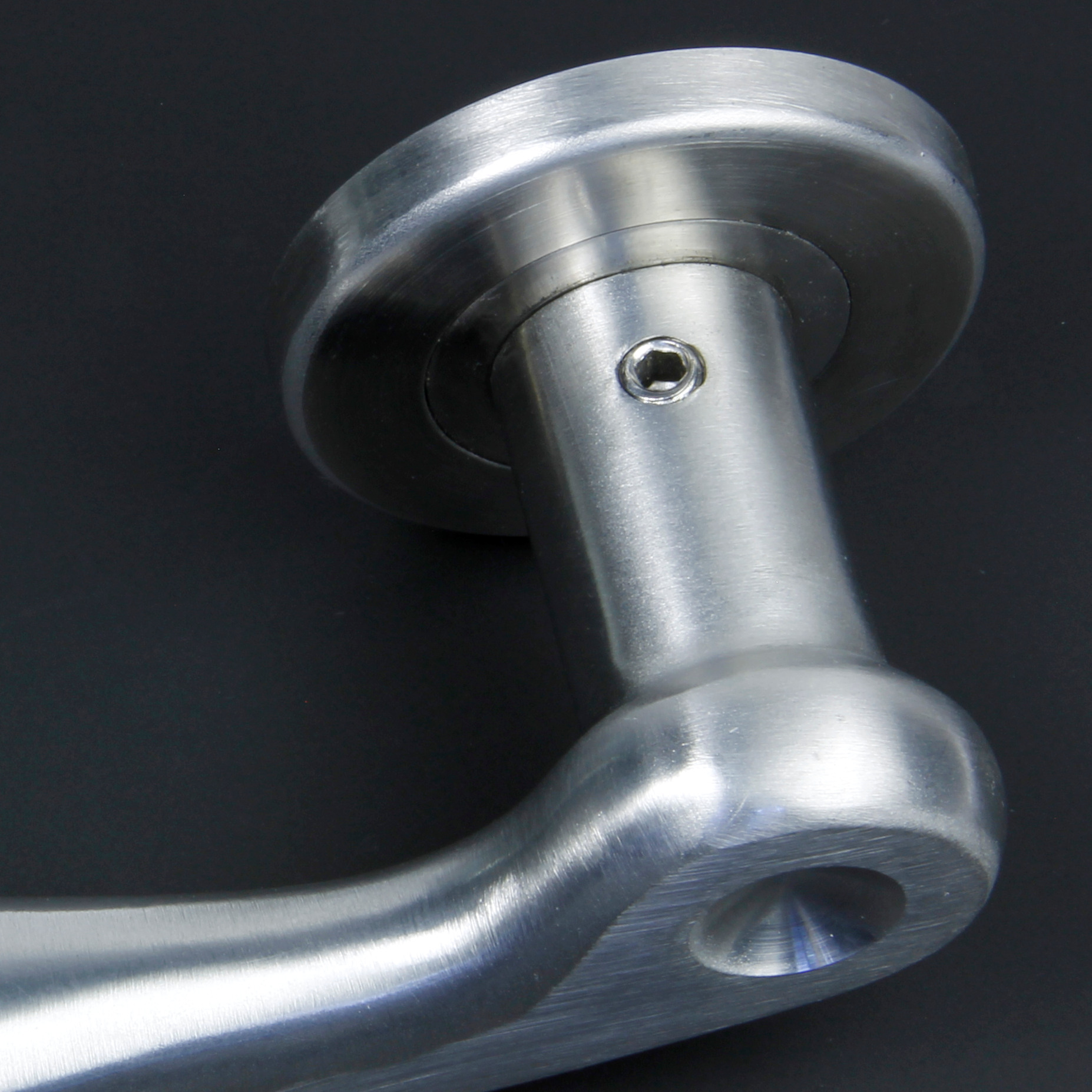
In an industrial environment grub screws are commonly used for locking components into position on shafts. The absence of a head ensures that the screw can sit descreetly below the surface of the assembled component. |
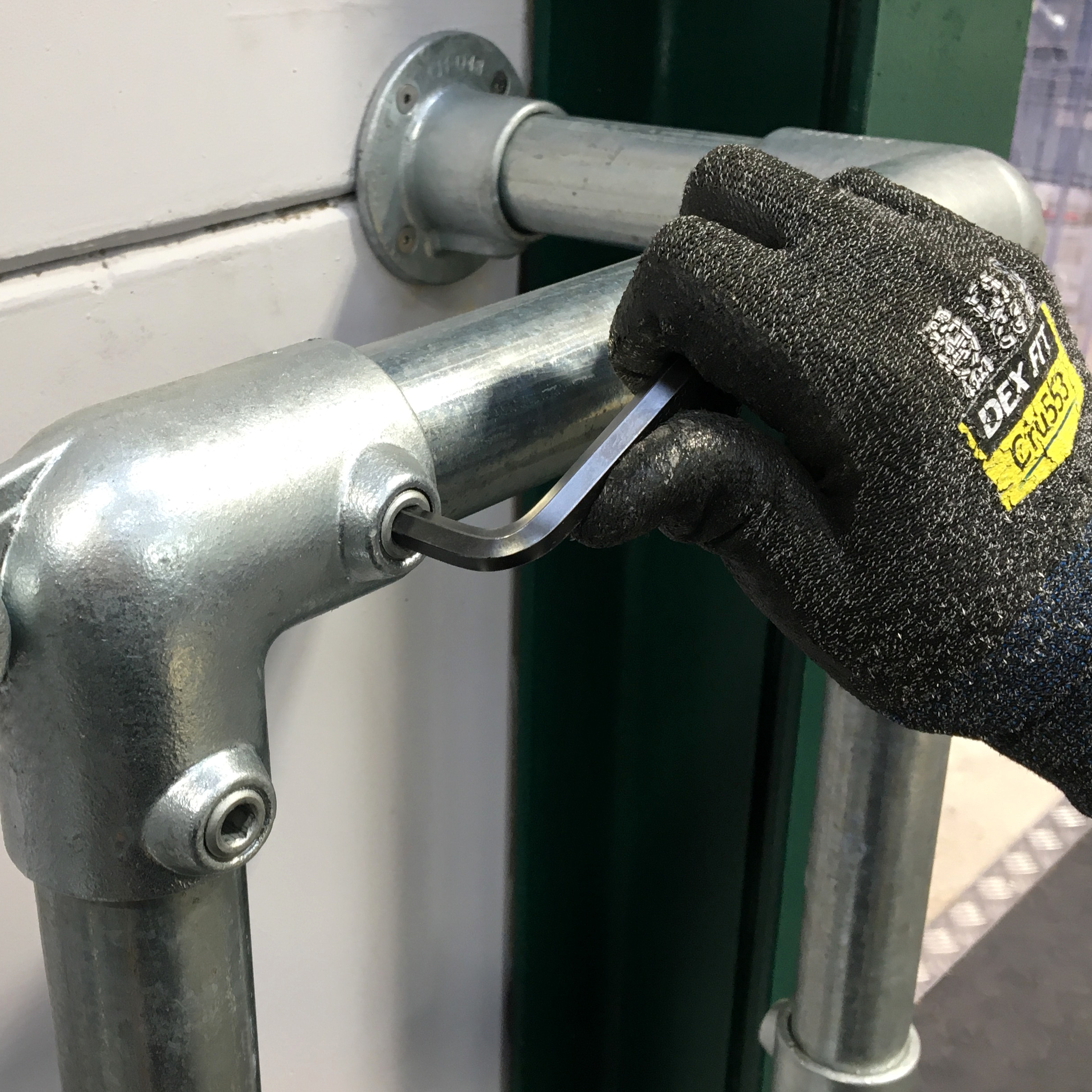
| Grub screws are commonly seen in door locking mechanisms and handles, and can be found domestically in bathroom fittings, curtain rails, light fittings and taps. |
 |
Are there other names for Grub Screws?
Grub Screws have a number of alternative names, including:
- Set Screws or setscrews
- Socket Set Screws
- Blind Screws
Please note that the phrase "set screw" can also refer to a fully threaded hex bolt in some markets around the world.
How to secure a Grub Screw?
| Grub screws are secured using a hex or allen key, but some types will require a slotted screwdriver. Other drives include Torx or 6 lobe , and square socket (known as a Robertson drive). |
|
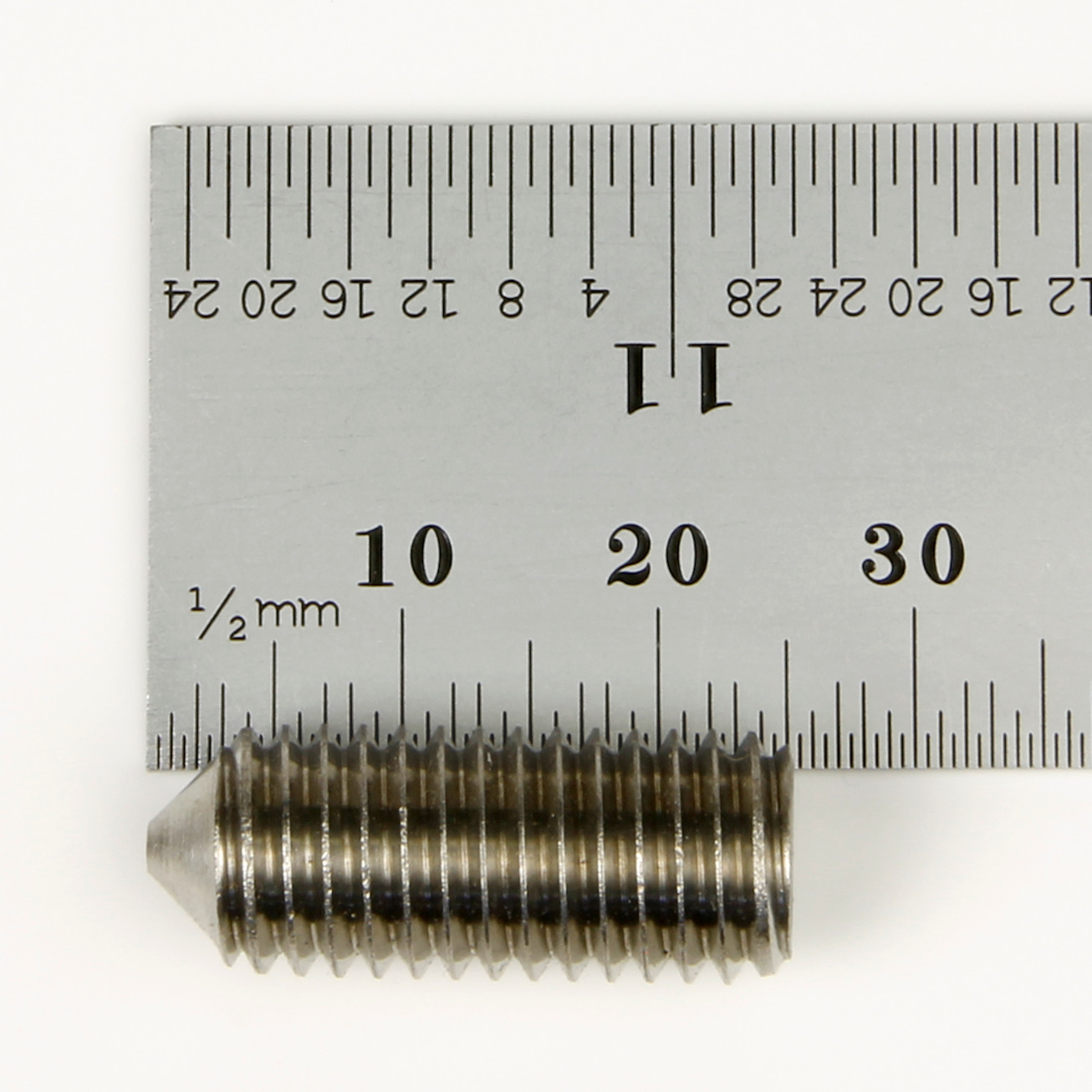
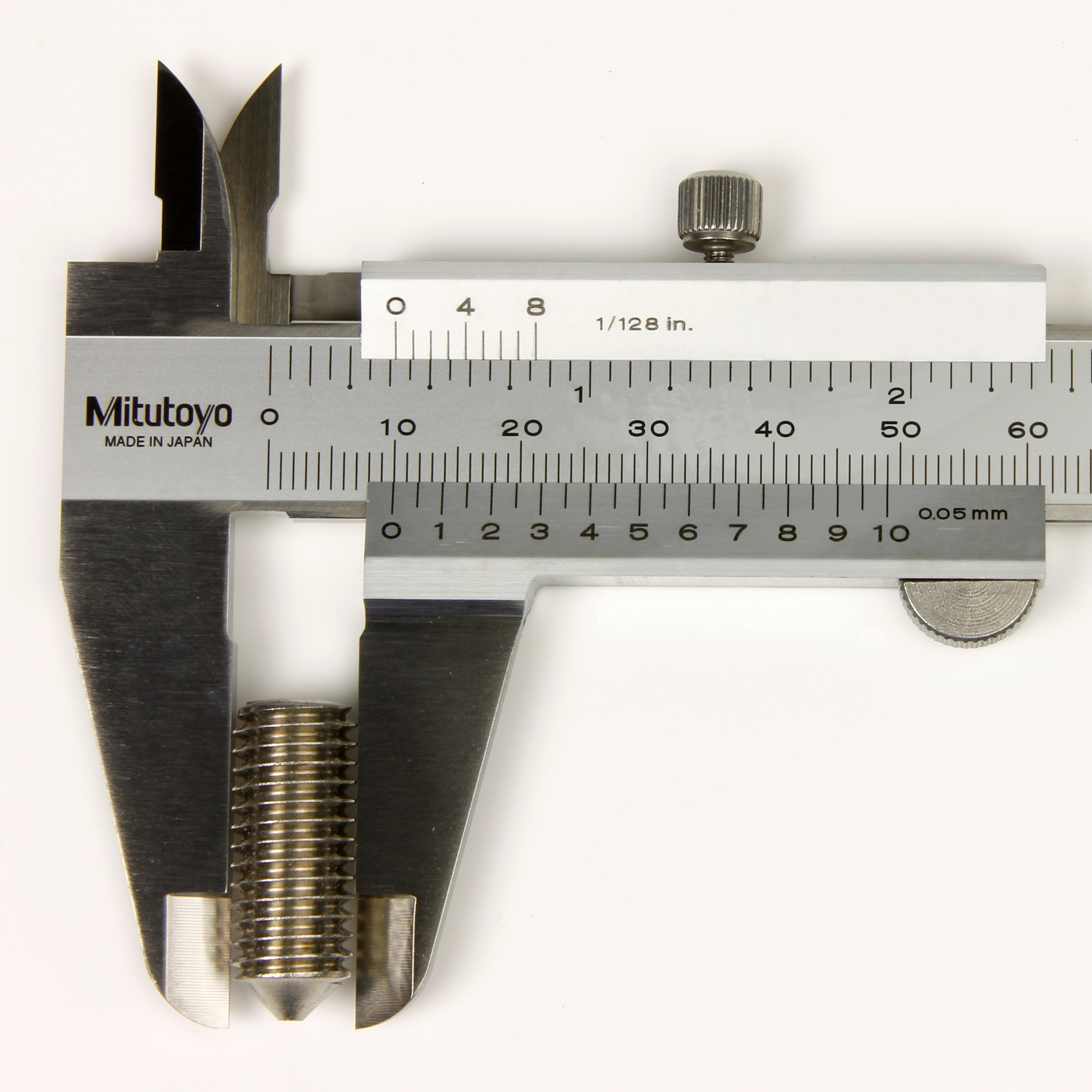
How do you measure a Grub Screw?
|
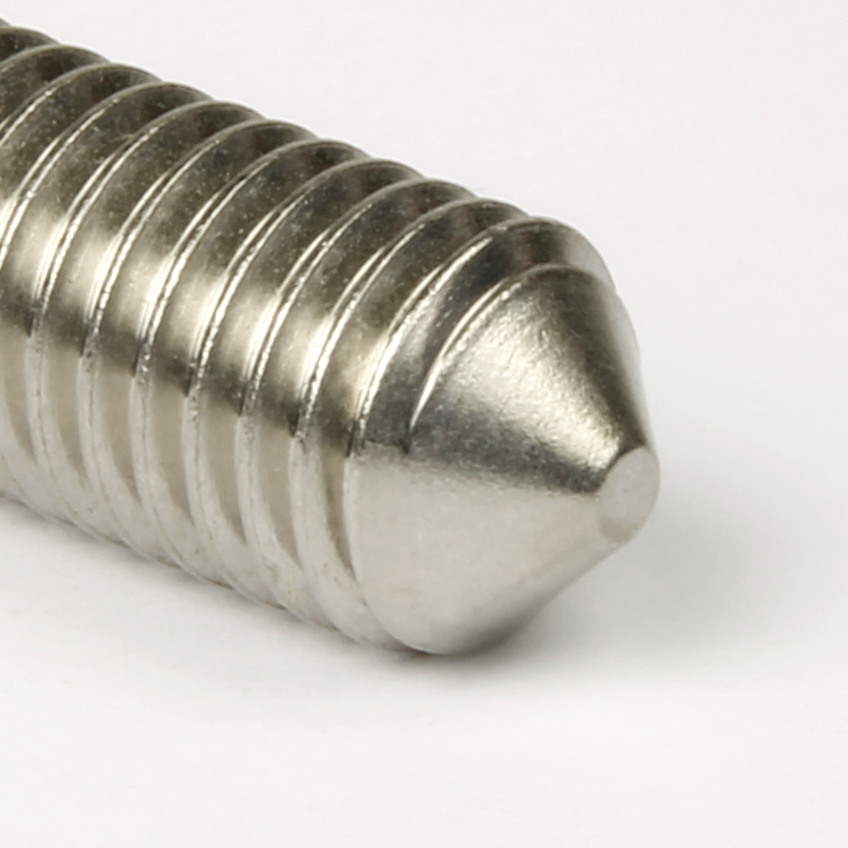
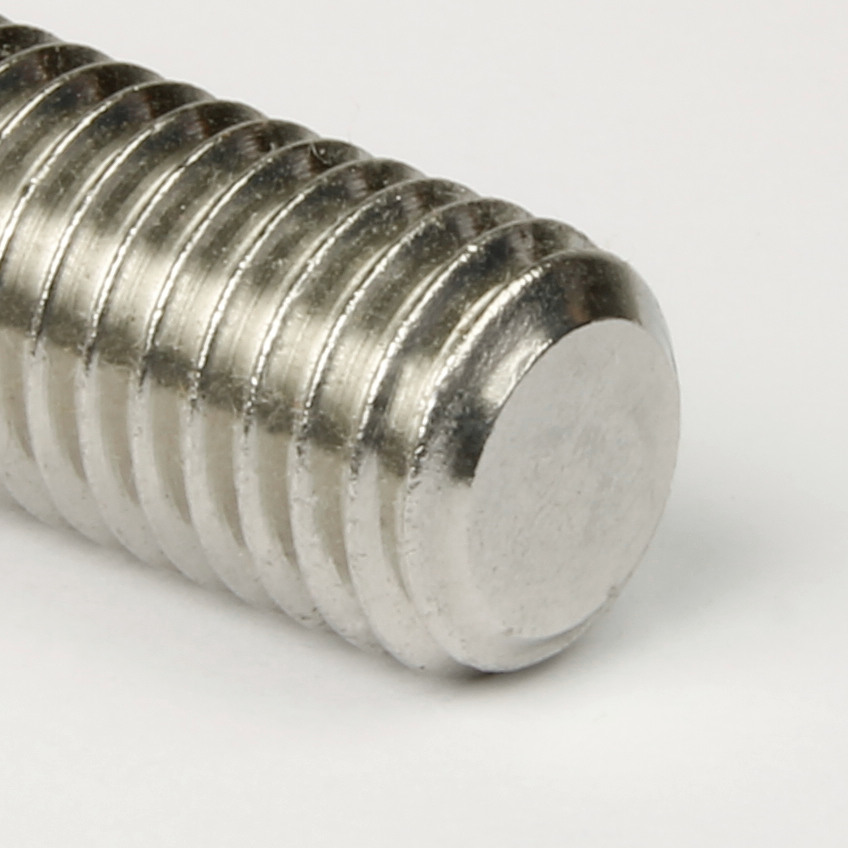
Grub Screw length is measured from end to end, including the point. The length of a grub screw can be measured perfectly satisfactorily with a standard ruler or tape measure. The example shown in the image is 25mm in length. |
| The diameter of a Grub Screw is best measured with vernier calipers or a micrometer and will be slightly less than the nominal diameter. The M10 standard coarse pitch example shown in the image will measure between 9.732mm and 9.968mm. |
|
What types of Grub Screw are there?
Grub screws are available in a number of different types. The 4 most common profiles or types are:
- cone point
- flat point
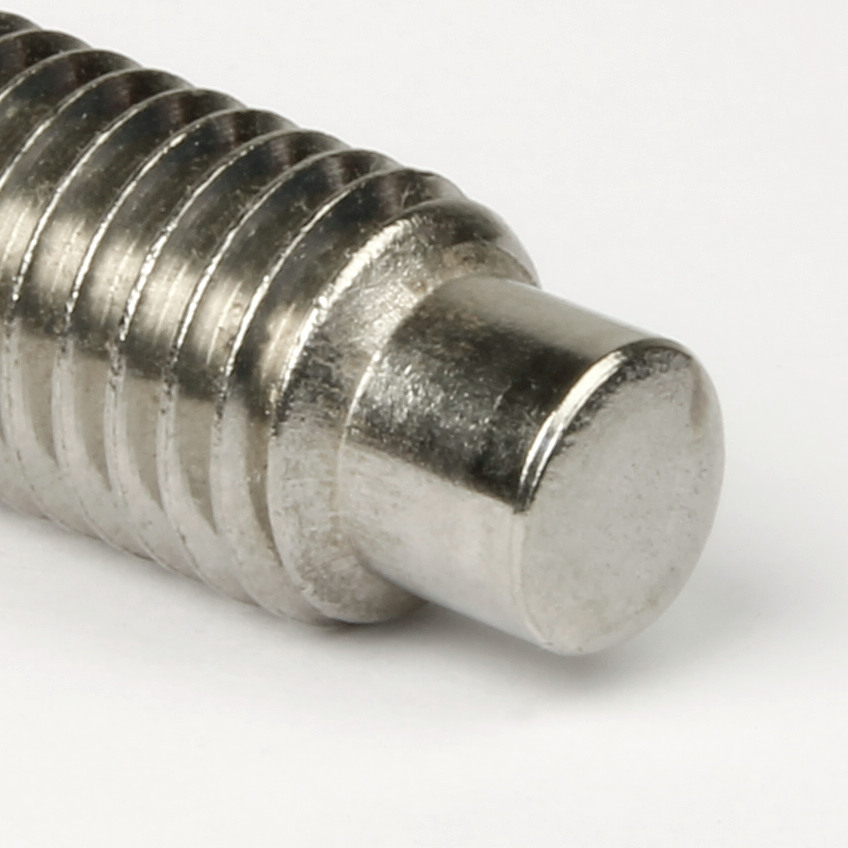
- dog point
- cup point
|
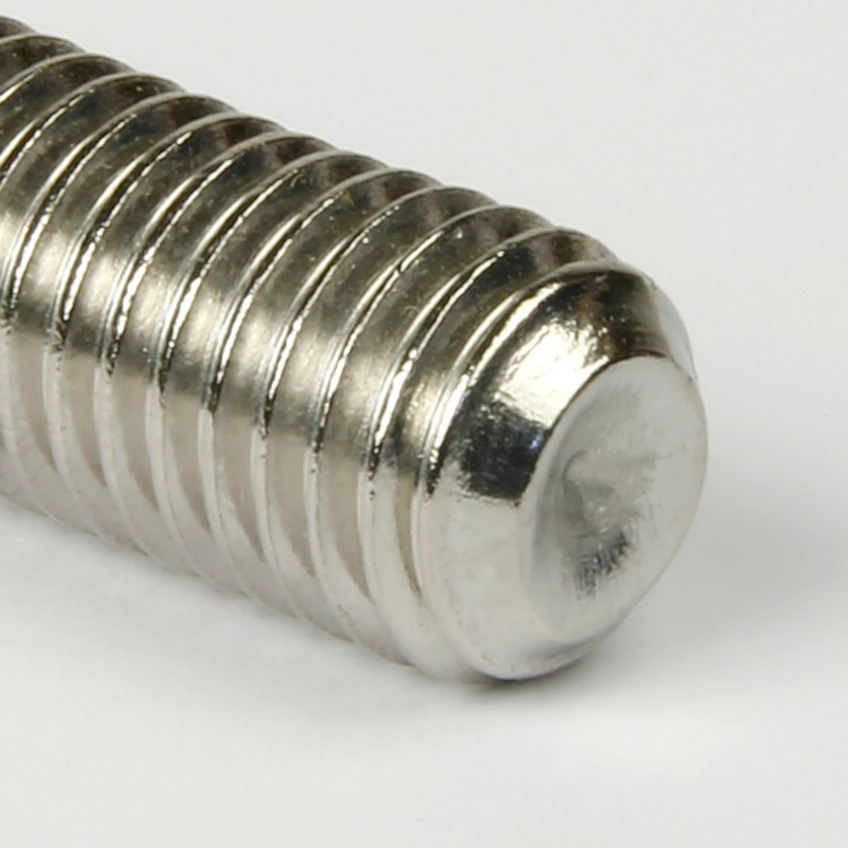
Cup point grub screws include a concave depression at one end, offering a similar function to the cone point, but can be driven in further, providing more torque and gripping force to the adjoining surface. The cup point is the most widely used profile. The curved edges of the cone spread the contact area, lessening the stress on the adjoining surface. Cup point grub screws with metric threads conform to DIN 916 and ISO 4029. |
| View Cup Point Grub Screw sizes and materials |
|
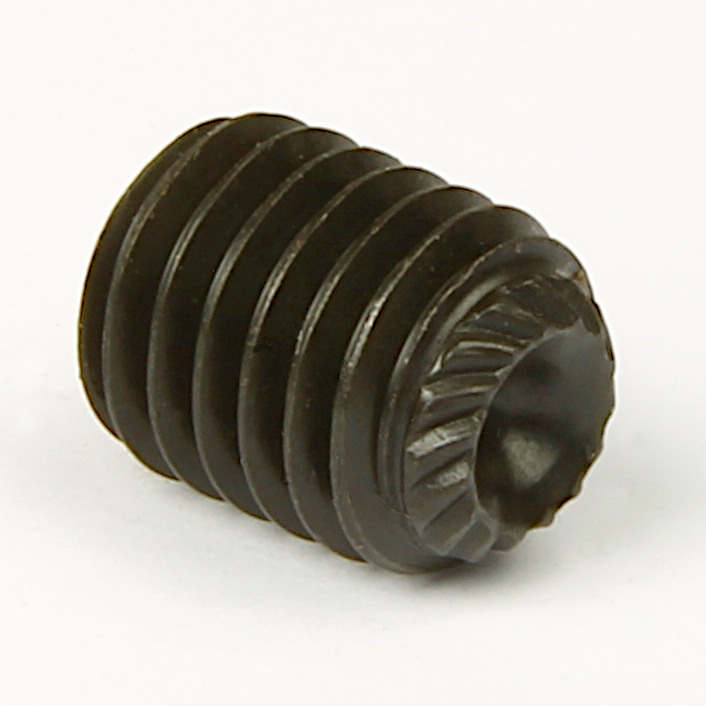
Knurled cup point grub screws are the knurled cousin of the standard cup point grub screw. The knurled feature helps reduce loosening from vibration. The knurls consist of angled ridges on the edge of the cup surface that, when tightened, have a ratchet-locking action as they cut into the mating component. Knurled cup point grub screws cannot be effectively reused as the cutting edges of the knurls are deflected or deformed when tightened on fitting. |
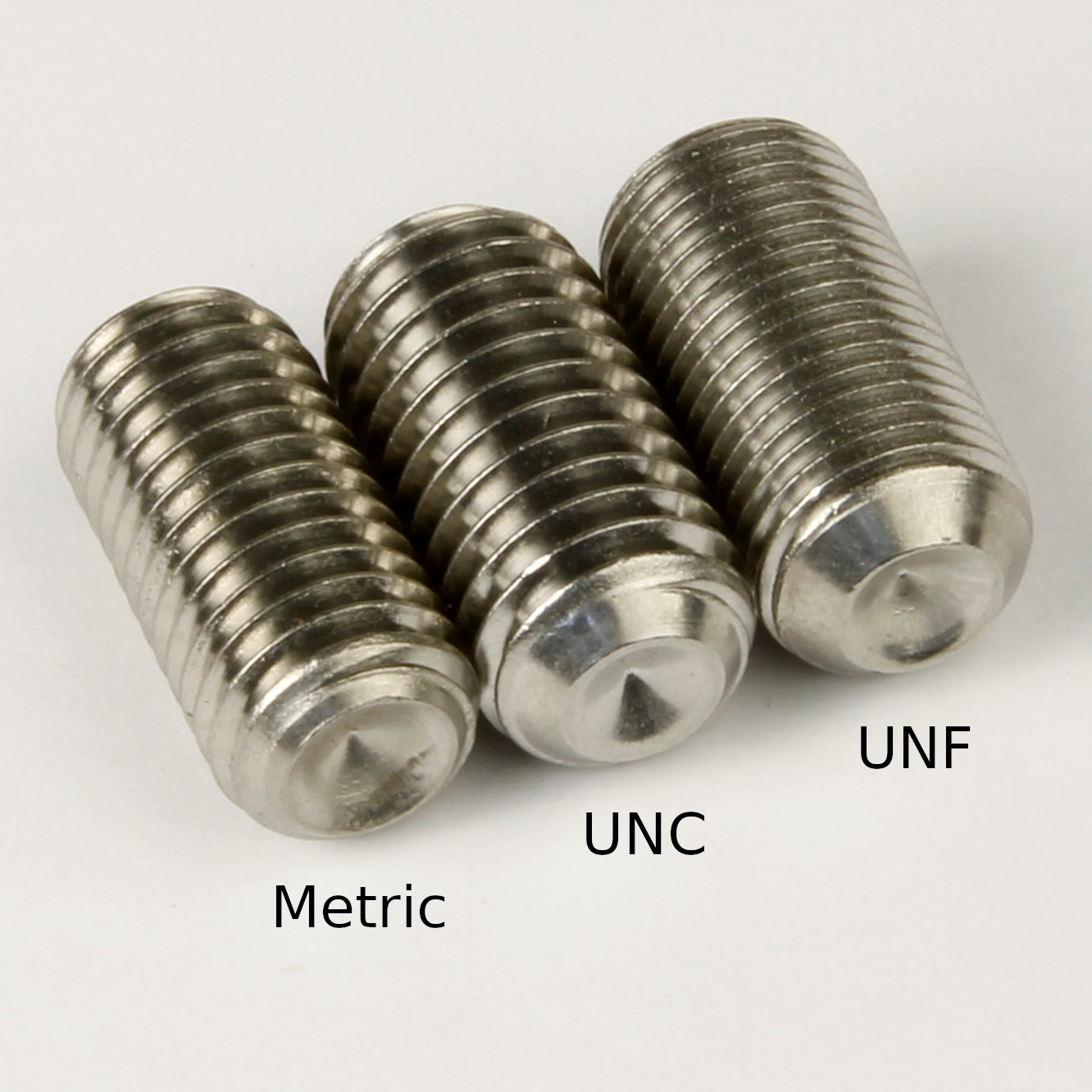
Thread pitch types of grub screws
How Strong are Grub Screws?
Grub screws are not rated for tensile strength like other threaded fasteners, as they are designed for compression rather than tensile loading.
Instead they are given a hardness rating. The Rockwell hardness measure is used to express the strength of a grub screw. 45H is the standard hardness for steel grub screws manufactured to the relevant ISO or DIN standard mentioned above, whereas stainless steel equivalents are less hard in comparison and rated 21H according to the same standard.
The strength specifications of grub screws manufactured to ASME B18.3 are defined in ASTM F912 for steel alloy and ASTM F880 for stainless steel.